South Korean Won: KRW stabilizes after South Korean Parliament axes martial law call
- The KRW shattered on Tuesday after SK President declared martial law.
- SK President Yoon Suk Yeol’s martial law call ran aground of South Korean lawmakers.
- The KRW plunged to its lowest levels since mid-2023 after political turmoil.
South Korea’s conservative President Yoon Suk Yeol declared “emergency martial law” early Tuesday in a surprise move that rattled equities with exposure to South Korean markets. South Korea’s President accused the country’s opposition Democratic Party of sympathizing with North Korea and undermining South Korea’s parliament with anti-state activities.
South Korea’s Parliament stepped in hours after President Yoon Suk Yeol’s announcement to soundly reject the South Korean President’s call for martial law. The South Korean Won stabilized slightly, paring back the day’s losses to settle USD/KRW near 1420.00 after the day’s early spike into 1445.00 early Tuesday.
President Yook Suk Yeol has been embroiled in a fierce battle with the opposition party, which is broadly favored to win the next election in 2027. South Korea’s Democratic Party has been pushing for impeachment articles against top conservative officials in prosecutor positions after President Yoon Suk Yeol rejected calls for investigations into multiple government scandals perpetrated by the South Korean President’s wife and several top officials within the conservative People Power Party.
USD/KRW daily chart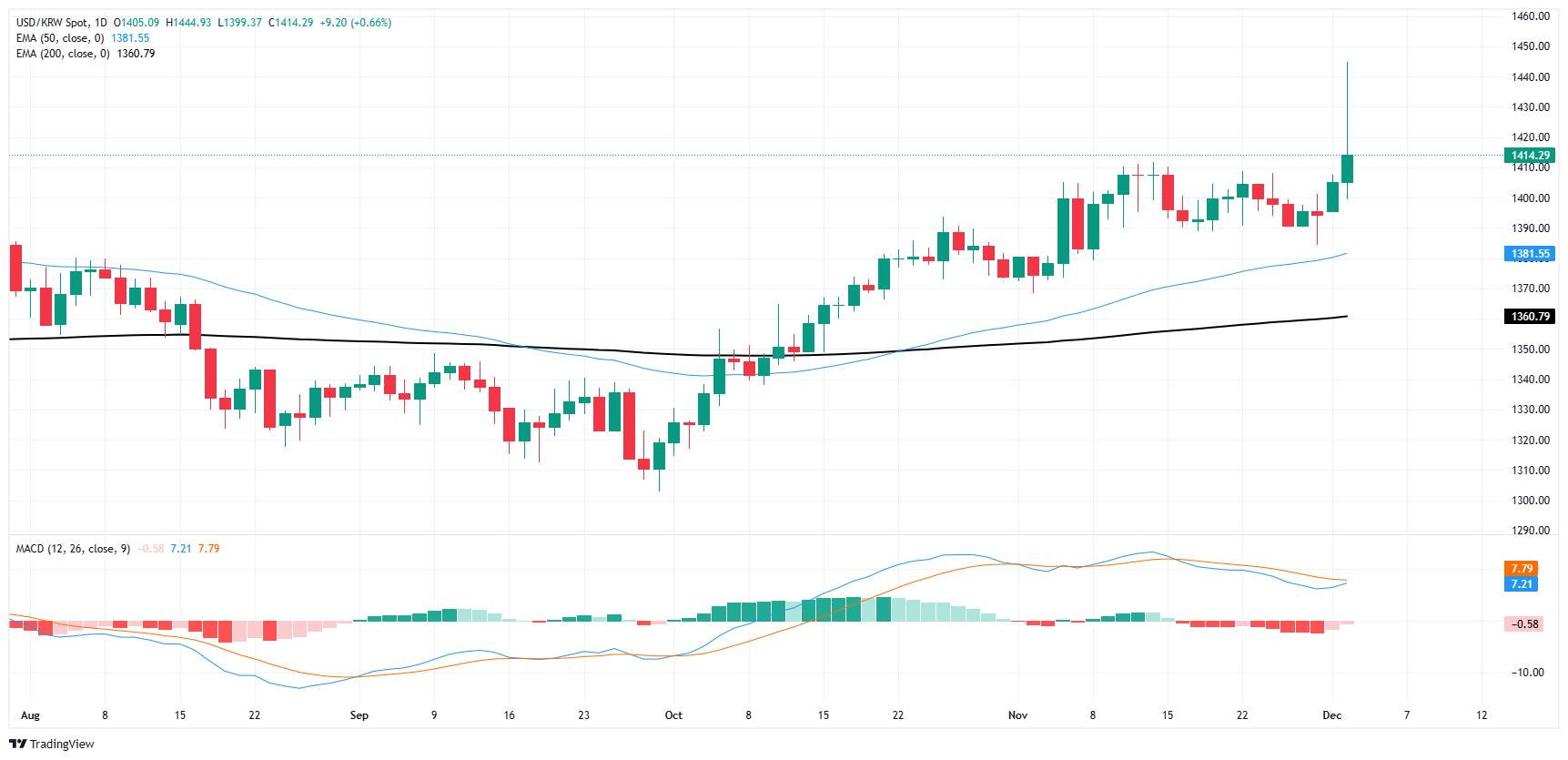
Risk sentiment FAQs
In the world of financial jargon the two widely used terms “risk-on” and “risk off'' refer to the level of risk that investors are willing to stomach during the period referenced. In a “risk-on” market, investors are optimistic about the future and more willing to buy risky assets. In a “risk-off” market investors start to ‘play it safe’ because they are worried about the future, and therefore buy less risky assets that are more certain of bringing a return, even if it is relatively modest.
Typically, during periods of “risk-on”, stock markets will rise, most commodities – except Gold – will also gain in value, since they benefit from a positive growth outlook. The currencies of nations that are heavy commodity exporters strengthen because of increased demand, and Cryptocurrencies rise. In a “risk-off” market, Bonds go up – especially major government Bonds – Gold shines, and safe-haven currencies such as the Japanese Yen, Swiss Franc and US Dollar all benefit.
The Australian Dollar (AUD), the Canadian Dollar (CAD), the New Zealand Dollar (NZD) and minor FX like the Ruble (RUB) and the South African Rand (ZAR), all tend to rise in markets that are “risk-on”. This is because the economies of these currencies are heavily reliant on commodity exports for growth, and commodities tend to rise in price during risk-on periods. This is because investors foresee greater demand for raw materials in the future due to heightened economic activity.
The major currencies that tend to rise during periods of “risk-off” are the US Dollar (USD), the Japanese Yen (JPY) and the Swiss Franc (CHF). The US Dollar, because it is the world’s reserve currency, and because in times of crisis investors buy US government debt, which is seen as safe because the largest economy in the world is unlikely to default. The Yen, from increased demand for Japanese government bonds, because a high proportion are held by domestic investors who are unlikely to dump them – even in a crisis. The Swiss Franc, because strict Swiss banking laws offer investors enhanced capital protection.